 栈的排序
栈的排序
问题描述:
请编写一个程序,按升序对栈进行排序(即最大元素位于栈顶),要求最多只能使用一个额外的栈存放临时数据,但不得将元素复制到别的数据结构中。 给定一个int数组 numbers,其中第一个元素为栈顶,请返回排序后的栈。请注意这是一个栈,意味着排序过程中你只能访问到第一个元素。 测试样例: 1,2,3,4,5 返回:5,4,3,2,1
- 思路分析:
我们可以使用额外的栈来进行数据的缓冲,当右边的栈(目标栈)的元素为空的时候我们需要将左边的栈(原栈)中的元素直接压入到右边的栈中,右边的栈不为空的情况下,我们需要弹出左边栈顶的元素,与右边栈顶元素进行比较如果大于等于右边栈顶的元素,直接压入到右边的栈中,假如小于,那么我们需要把右边栈中所有大于左边栈弹出来的元素都压入到左边的堆栈中,所以这里可以使用一个while循环进行右边元素压入到左边元素的操作,等到while循环结束那么将弹出来的元素压入到右边的堆栈中,当所有的元素都压入到右边的堆栈中那么我们就得到了排好序之后的目标栈了
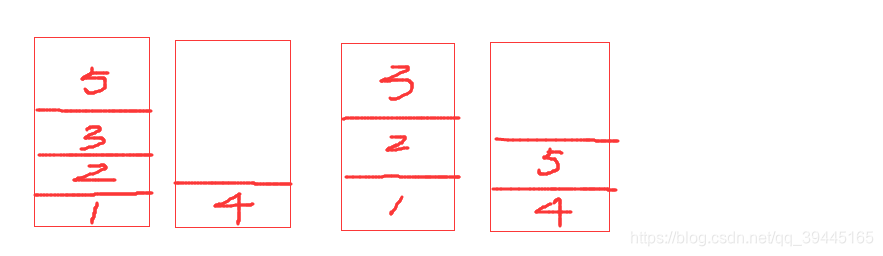
思路清楚之后代码就比较简单了,其中主要是一些栈的方法的调用和简单的逻辑判断
这里要注意不要混淆栈顶元素的弹出方法pop()和栈顶元素的查看方法peek(),一个是弹出栈顶元素,另外一个是查看栈顶元素但是不弹出
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {10, 5, 4, 14, 3, 2, 1, 8};
twoStackSort(arr);
}
private static void twoStackSort(int[] arr){
Stack<Integer> source = new Stack<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
source.push(arr[i]);
}
Stack<Integer> target = twoStackSort(source);
while(!target.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(target.pop());
}
}
排序栈
private static Stack<Integer> twoStackSort(Stack<Integer> source) {
Stack<Integer> target = new Stack<Integer>();
while(!source.isEmpty()){
if(target.isEmpty()){
target.push(source.pop());
}else{
int v = source.pop();
if(target.peek() <= v){
target.push(v);
}else{
while(!target.isEmpty() && target.peek() > v){
source.push(target.pop());
}
target.push(v);
}
}
}
return target;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
此方法是直接借助另外一个栈,如果使用优先级队列的话就更简单
上次更新: 2024/08/09, 16:07:34
